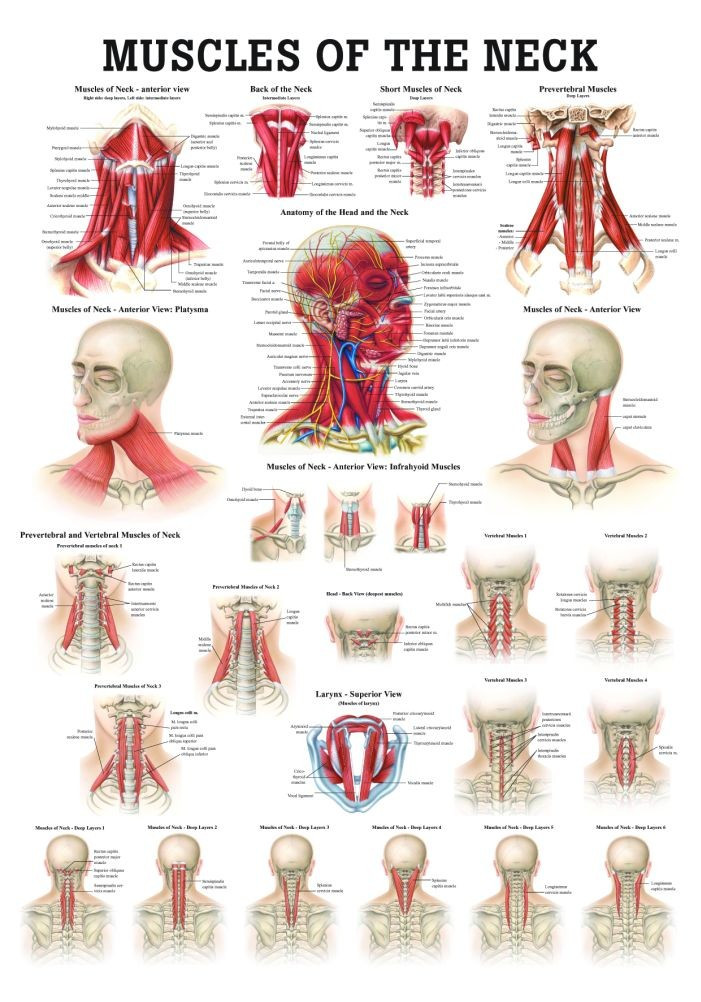
Back Of Neck Anatomy - Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid anterior vertebral muscles:. This article concerning the anatomy of the head and neck area gives you a clear structure at hand to see anatomy and function of the regions of the lower face. The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. The longus capitis and rectus capitis anterior are the direct antagonists of the muscles at the back of the neck, serving to restore the head to its natural position after it has been drawn backward. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back. The splenius muscles originate at the midline and run laterally and superiorly to their insertions. The spine runs from the base of your skull down the length of your back, going all the way down to your pelvis. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back. Your neck is like no other part of the vertebral spinal column and enables your head and neck a wide range of motion. Despite being a relatively small region, it contains a range of important anatomical features. When most people mention their back, what they are actually referring to is their spine. All of the anatomical structures of the face with labels on 150 axial and coronal slices from a scan: Use the mouse scroll wheel to move the images up and down alternatively use the tiny arrows (>>) on both side of the image to move the images. Foundational anatomy provides medical students with the necessary background in anatomy for success in clerkships. The neck is the area between the skull base and the clavicles. So many muscles that cause migraines, arm, neck, shoulders, and back pain. The anterior jugular vein (v. 12 photos of the anatomy of the back of the neck. The splenius muscles originate at the midline and run laterally and superiorly to their insertions. It runs down the back part of the neck, and opens into the external jugular vein just below the middle of its course. Some important structures contained in or passing through the neck include the seven cervical vertebrae and enclosed spinal cord, the jugular veins and carotid arteries, part of the esophagus, the larynx. The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. Neck muscles help support the cervical spine and contribute to movements of the head, neck, upper back, and shoulders. Learn about these muscles, their locations & functional the traps are quite a complex set of muscles. Surface anatomy and surface markings bibliographic record list of illustrations subject index. Clinically, surface anatomy is used to split the neck into anterior and posterior triangles which provide clues as to the location of specific structures. The spine runs from the base of your skull down the length of your back, going all the way down to your pelvis. Understanding the anatomy of your cervical spine and the vital nerves it contains should motivate you to adopt behaviors that help prevent neck injury and. Anterior muscles of the neck. Despite being a relatively small region, it contains a range of important anatomical features. We've largely focused on the physical aspect of our spinal anatomy in this series. Your neck is like no other part of the vertebral spinal column and enables your head and neck a wide range of motion. Anterior muscles of the neck. Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid anterior vertebral muscles: Choose from 500 different sets of flashcards about neck anatomy back neck upper on quizlet. Use the mouse scroll wheel to move the images up and down alternatively use the tiny arrows (>>) on both side of the image to move the images. All of the anatomical structures of the face with labels on 150 axial and coronal slices from a scan: This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat. Neck, in land vertebrates, the portion of the body joining the head to the shoulders and chest. Digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, stylohyoid infrahyoid muscles: In radiology, the 'head and neck' refers to all the anatomical structures in this region excluding the central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal co. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back. Anatomy of the head and neck: Top head neck anatomy flashcards ranked by quality. The posterior muscles of the neck are primarily concerned with head movements, like extension. So many muscles that cause migraines, arm, neck, shoulders, and back pain. When most people mention their back, what they are actually referring to is their spine. A dynamic and interactive atlas of ent imaging. It runs down the back part of the neck, and opens into the external jugular vein just below the middle of its course. The head rests on the top part of the vertebral column, with the skull joining at c1. A collection of anatomy notes covering the key anatomy concepts that medical students need to learn. Foundational anatomy provides medical students with the necessary background in anatomy for success in clerkships. The neck is the part of the body that separates the head from the torso. Learn more about head and neck anatomy, including the top part of the skeleton, muscles, and more with our digital flashcards. This article concerning the anatomy of the head and neck area gives you a clear structure at hand to see anatomy and function of the regions of the lower face. Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid anterior vertebral muscles: When most people mention their back, what they are actually referring to is their spine. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back. All of the anatomical structures of the face with labels on 150 axial and coronal slices from a scan: The back anatomy includes the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, erector spinae, rhomboid, & teres major.
Foundational anatomy provides medical students with the necessary background in anatomy for success in clerkships.
Clinically, surface anatomy is used to split the neck into anterior and posterior triangles which provide clues as to the location of specific structures.
Some important structures contained in or passing through the neck include the seven cervical vertebrae and enclosed spinal cord, the jugular veins and carotid arteries, part of the esophagus, the larynx.
Back Of Neck Anatomy - Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid anterior vertebral muscles:. This article concerning the anatomy of the head and neck area gives you a clear structure at hand to see anatomy and function of the regions of the lower face. The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. The longus capitis and rectus capitis anterior are the direct antagonists of the muscles at the back of the neck, serving to restore the head to its natural position after it has been drawn backward. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back. The splenius muscles originate at the midline and run laterally and superiorly to their insertions.
The spine runs from the base of your skull down the length of your back, going all the way down to your pelvis. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back. Your neck is like no other part of the vertebral spinal column and enables your head and neck a wide range of motion. Despite being a relatively small region, it contains a range of important anatomical features. When most people mention their back, what they are actually referring to is their spine.

Foundational anatomy provides medical students with the necessary background in anatomy for success in clerkships.
All of the anatomical structures of the face with labels on 150 axial and coronal slices from a scan: Use the mouse scroll wheel to move the images up and down alternatively use the tiny arrows (>>) on both side of the image to move the images. Foundational anatomy provides medical students with the necessary background in anatomy for success in clerkships. The neck is the area between the skull base and the clavicles. So many muscles that cause migraines, arm, neck, shoulders, and back pain. The anterior jugular vein (v. 12 photos of the anatomy of the back of the neck. The splenius muscles originate at the midline and run laterally and superiorly to their insertions. It runs down the back part of the neck, and opens into the external jugular vein just below the middle of its course. Some important structures contained in or passing through the neck include the seven cervical vertebrae and enclosed spinal cord, the jugular veins and carotid arteries, part of the esophagus, the larynx. The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. Neck muscles help support the cervical spine and contribute to movements of the head, neck, upper back, and shoulders. Learn about these muscles, their locations & functional the traps are quite a complex set of muscles.
Surface anatomy and surface markings bibliographic record list of illustrations subject index. Clinically, surface anatomy is used to split the neck into anterior and posterior triangles which provide clues as to the location of specific structures. The spine runs from the base of your skull down the length of your back, going all the way down to your pelvis. Understanding the anatomy of your cervical spine and the vital nerves it contains should motivate you to adopt behaviors that help prevent neck injury and. Anterior muscles of the neck.
Clinically, surface anatomy is used to split the neck into anterior and posterior triangles which provide clues as to the location of specific structures.
Despite being a relatively small region, it contains a range of important anatomical features. We've largely focused on the physical aspect of our spinal anatomy in this series. Your neck is like no other part of the vertebral spinal column and enables your head and neck a wide range of motion. Anterior muscles of the neck. Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid anterior vertebral muscles: Choose from 500 different sets of flashcards about neck anatomy back neck upper on quizlet. Use the mouse scroll wheel to move the images up and down alternatively use the tiny arrows (>>) on both side of the image to move the images. All of the anatomical structures of the face with labels on 150 axial and coronal slices from a scan: This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat. Neck, in land vertebrates, the portion of the body joining the head to the shoulders and chest. Digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, stylohyoid infrahyoid muscles: In radiology, the 'head and neck' refers to all the anatomical structures in this region excluding the central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal co. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back.
Anatomy of the head and neck: Top head neck anatomy flashcards ranked by quality. The posterior muscles of the neck are primarily concerned with head movements, like extension. So many muscles that cause migraines, arm, neck, shoulders, and back pain. When most people mention their back, what they are actually referring to is their spine.

Some important structures contained in or passing through the neck include the seven cervical vertebrae and enclosed spinal cord, the jugular veins and carotid arteries, part of the esophagus, the larynx.
A dynamic and interactive atlas of ent imaging. It runs down the back part of the neck, and opens into the external jugular vein just below the middle of its course. The head rests on the top part of the vertebral column, with the skull joining at c1. A collection of anatomy notes covering the key anatomy concepts that medical students need to learn. Foundational anatomy provides medical students with the necessary background in anatomy for success in clerkships. The neck is the part of the body that separates the head from the torso. Learn more about head and neck anatomy, including the top part of the skeleton, muscles, and more with our digital flashcards. This article concerning the anatomy of the head and neck area gives you a clear structure at hand to see anatomy and function of the regions of the lower face. Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid anterior vertebral muscles: When most people mention their back, what they are actually referring to is their spine. Muscles of the posterior neck and the back. All of the anatomical structures of the face with labels on 150 axial and coronal slices from a scan: The back anatomy includes the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, erector spinae, rhomboid, & teres major.
0 comments:
Post a Comment